Road freight transport is considered to be one of the best options at national level for commercial transactions and 95% of businesses use it for its speed and safety.
Advantages of road transportation
- Faster compared to rail and sea transport.
- On short journeys it is more economical.
- It is a more flexible and versatile option.
- This is a type of transfer of goods to the final consignee, i.e. a transfer from origin to destination, without interference.
- Any kind of goods can be transported.
Contract for the carriage of goods by road
The contract for the carriage of goods by road consists of a prior agreement (preferably in writing) between the carrier who agrees to load goods of any kind and their subsequent carriage by road until unloading at the agreed destination. This agreement is made in exchange for economic consideration and using a self-propelled vehicle.
In this document, the prices and expenses that may be incurred by both parties are agreed upon, as well as the date and time of loading, unloading, type of goods, details of the consignee and all the requirements associated with such transport.
There are two types of contract of carriage:
- Transport by expedition:Contract for a single service. They are of an eventual type.
- Continuous transport: Continuous transport contracts established over a specified period of time.
Consignment note
The consignment note is a legal document containing the terms and conditions of carriage and security clauses. It is not an indispensable document, but both parties may request the formalization of such a document.
It is issued by the road haulage company and serves as a receipt for goods, i.e. it indicates the delivered goods and their general condition. Also, it is a proof of transport and serves as an agreement between both parties prior to billing to know the amount of the service performed.
As well as, it also indicates what kind of merchandise is being hired, if it is transported by full truck, groupages…
What is a groupage?
A groupage is the grouping of goods from different customers in order to fill the transport lorry, since the quantity of a single journey is insufficient and cannot fill a whole container.
This type of trip not only saves space in the transport of goods by road and takes advantage of the container, but also reduces costs and maximizes the work and/or trip, as well as the productivity of a single vehicle compared to a container that offers only one trip.
Liability of the carrier
In the transport contract, you not only have the obligation to provide a service, but you also undertake to carry the goods from the point of origin to the point of destination under previously agreed conditions and without any damage or damage to the goods.
In the event of damage, loss or damage to the goods, the carrier shall be liable financially. If there is a delay in the delivery of the goods, you will also be liable in that situation.
This responsibility is inescapable on both sides and is provided for by law, which means that these obligations cannot be circumvented or delimited by complying with the collective agreement for the carriage of goods by road.
Road transport of dangerous goods
What are dangerous goods? They are those that may pose a risk to both the environment and people. The most common materials are: radioactive material, explosives, flammable or toxic gases, corrosive material…
Similar to special transport, the transport of dangerous goods is subject to a number of legal requirements for safety reasons. In order to protect the environment and drivers, there are European regulations governing driving when transporting dangerous goods: ADR.
ADR is a European Agreement on the Transport of Goods that regulates the transport of dangerous goods.
This agreement regulates the documentation, transportation and packaging of these goods, including loading, unloading and storage. In order to protect the environment and people, the obligations and responsibilities that this agreement entails must be fulfilled.
Vehicles carrying this type of goods must be identified with an ADR certificate, as it certifies that they are authorized for this transport. This type of certificate obliges the vehicle to meet a number of requirements such as having an independent battery disconnector, armored electrical installation, fire extinguishers…
These vehicles must bear at the rear of the vehicle, as well as at the front, a marked orange sign for their identification.
- At the top, the type of hazard of the raw material being transported is indicated.
- At the bottom, the type of goods is indicated
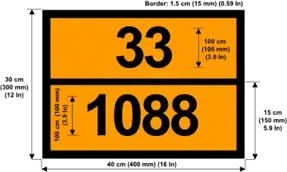
Another system for marking dangerous goods is the ADR pictogram system.
What are ADR pictograms?
These are square-shaped labels held by a vertex to indicate the type of goods being handled or transported.

They should always be on a background offering good contrast, surrounded by an edge at a distance of 5 mm and should have a size of 100 x 100 mm.
Rest and Driving Times Regulations
There are two regulations governing rests, driving times and breaks in road transport, as follows:
- Regulation EEC 3821/85 refers to the “compliance with the conditions of construction, installation, use and inspection” of recording equipment for transport vehicles.
- Regulation (EC) 561/2006 refers to the “road transport sector and the improvement of working conditions and road safety”.
Whether the journey is public or private, all drivers are subject to both regulations.
Driving times in transport
The driving times of the hauliers are divided into: daily, weekly and bi-weekly driving.
- Daily working day: The maximum driving time is 9h and you can only exceed the daily working day of 10h only 2 days a week. Working hours are therefore carried out in accordance with the rest hours of the hauliers and not on calendar days.
- Weekly working hours: You may not exceed 56 hours of driving per week. In this type of days, if they are counted as calendar days.
- Bi-weekly working day: You may not exceed 90 hours of driving twice a week, i.e. in periods of two weeks.
Rest breaks in road transport
There are three types of rest: daily, weekly and two consecutive weeks.
- Daily rest: You should rest 11h continuously. There is an exception, where you can rest 9h uninterrupted if you have already rested for 3h on the same day.
- Weekly rest: After driving for 6 days, you must take a break of 45 hours uninterrupted.
- Rest in two consecutive weeks: In the course of two weeks you must take two breaks of at least 45 hours. There is a reduced rest of 45 hours one week and 24 hours the next.
Pauses in road transport
These are the breaks that the driver must take throughout the day.
- Every 4 hours and 30 minutes of driving you have to take a break of 45 minutes.
- There is the option of making split stops with breaks of 30min and 15min always within the driving period of 4h and 30 minutes.
Maximum authorised mass
Each type of vehicle has a maximum authorised mass which may vary depending on its distance and axles.
- Two-axle truck: maximum weight of 18,000 kgs
- Three-axle trucks: maximum weight of 25 tons.
- Four-axle trucks: not exceeding 31 tonnes.
Recommendations for road transport
Below we leave you all the guidelines we use for a correct road trip and safe transport of your goods.
- We check the vehicles on a regular basis
- We plan the routes in advance of the trip to save time
- We comply with the rest times of our drivers. We don’t just take care of them, this way we take care of the safety and protection of your goods!
Do you still have doubts about road freight transport?
Do not hesitate to contact us and we will solve them for you!
Request your quote in less than 3 minutes with just one click.